The Color Wheel: Understanding the Basics of Color Theory
Colors have always been an essential part of human existence. They are everywhere - from the clothes we wear to the food we eat, from the environment we live in to the technology we use. Colors have the power to evoke emotions, change moods, and influence decisions. Understanding how colors work and how they interact with each other is essential for anyone working in design, art, marketing, or any other creative field. In this article, we will explore the basics of color theory and how to use the color wheel to create visually appealing designs.
What is the Color Wheel?
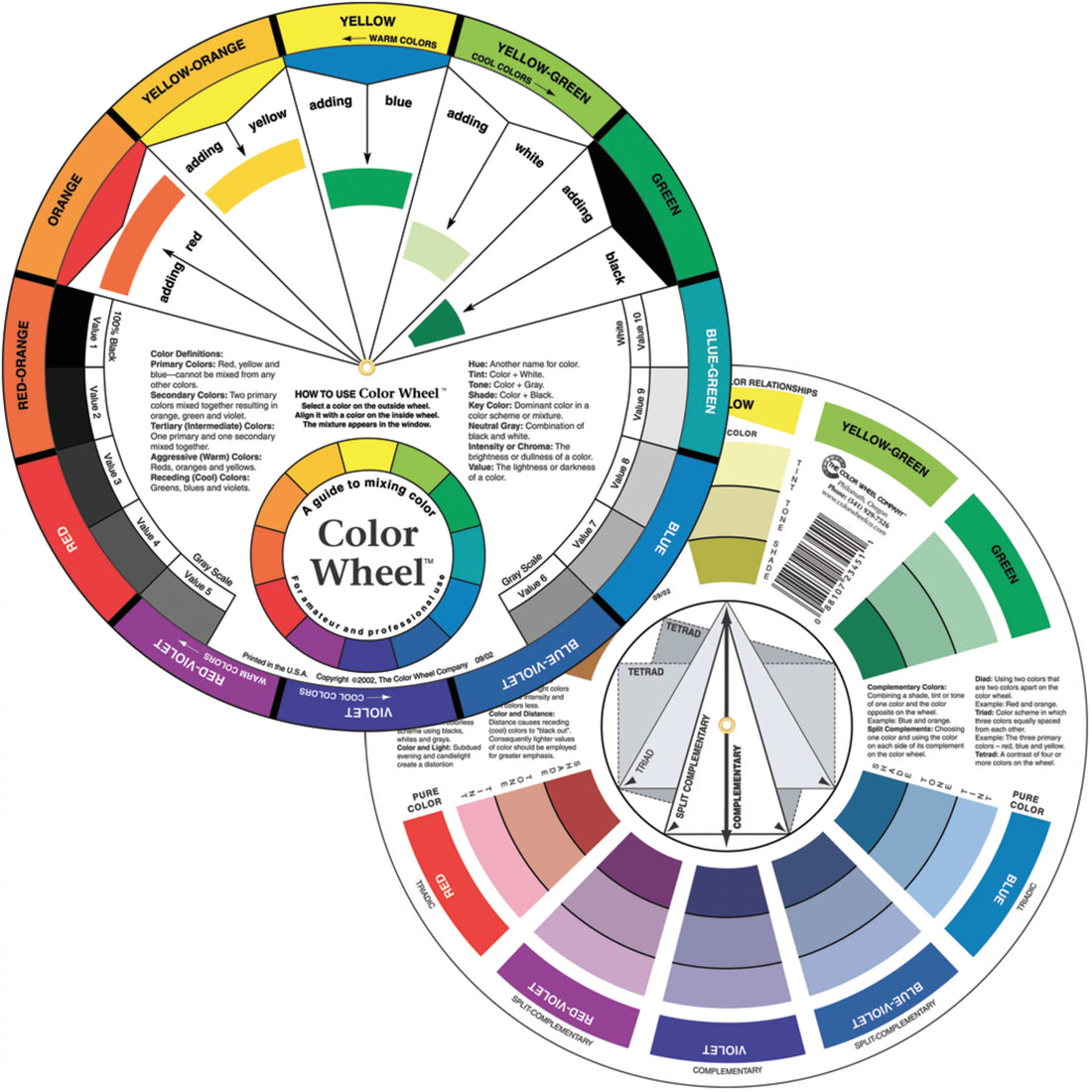
The color wheel is a visual representation of the relationships between colors. It is a tool used by artists, designers, and anyone working with color to create harmonious and aesthetically pleasing color schemes. The color wheel is divided into three primary sections: the primary colors, secondary colors, and tertiary colors.
Primary Colors
The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. They are called primary because they cannot be created by mixing any other colors together. All other colors can be created by mixing these three primary colors in different proportions.
Secondary Colors
Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors together. The three secondary colors are green (blue + yellow), purple (red + blue), and orange (red + yellow).
Tertiary Colors
Tertiary colors are created by mixing one primary color with one secondary color. They are located between the primary and secondary colors on the color wheel. There are six tertiary colors: yellow-green, blue-green, blue-purple, red-purple, red-orange, and yellow-orange.
Using the Color Wheel to Create Color Schemes
Now that we understand the basics of the color wheel, let's explore how we can use it to create visually appealing color schemes.
Monochromatic Color Scheme
A monochromatic color scheme uses variations of the same color. This creates a harmonious and calming effect. For example, a monochromatic color scheme for a website could use different shades of blue.
Analogous Color Scheme
An analogous color scheme uses colors that are adjacent to each other on the color wheel. This creates a natural and comfortable color combination. For example, an analogous color scheme could use yellow, yellow-green, and green.
Complementary Color Scheme
A complementary color scheme uses colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel. This creates a vibrant and eye-catching effect. For example, a complementary color scheme could use blue and orange.
Triadic Color Scheme
A triadic color scheme uses three colors that are evenly spaced on the color wheel. This creates a dynamic and balanced effect. For example, a triadic color scheme could use red, yellow, and blue.
Conclusion
The color wheel is an essential tool for anyone working with colors. It provides a visual representation of the relationships between colors and helps us create harmonious and aesthetically pleasing color schemes. Understanding the basics of color theory and the color wheel is essential for anyone working in design, art, marketing, or any other creative field.